What is a SMART City
SMART Cities are:
- Livable
- Alive
- Sustainable
- Innovative
- Leverage technology to serve people, society and the environment
- Connected and share information
- Designed to optimise resources and promote sustainable development.
Quiz
- What does a SMART city mean for you?
- Where is your SMART city?
- What is the name of your SMART city?
Exploring Sustainability – What Is It?
Many different points of view exist on Sustainability and how can be achieved. Here we will discuss a method commonly used to describe Sustainability – The Three Pillars of Sustainability.
The Three Pillars of Sustainability
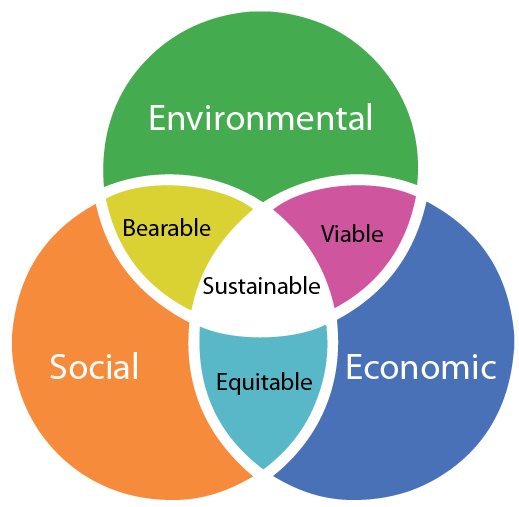
The three pillars of sustainability is a method of defining the sustainability problem and consists of three pillars economic, social, and environmental. In this model each pillar needs to be in balance for the system as a whole to be sustainable. (as illustrated in figure 1 below)
Quiz
How would you use this model to explore the sustainability of your SMART City?
Systems Thinking & Feedback
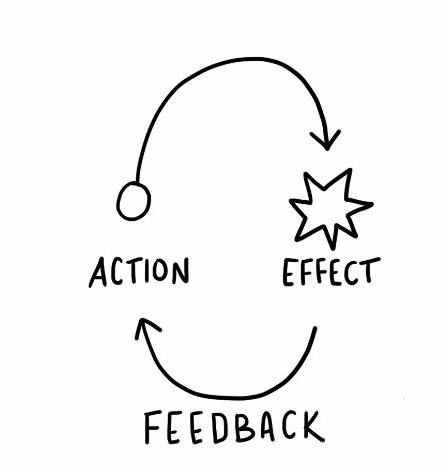
Systems thinking is a method that helps us to better understand a system by looking at the elements of the system and interactions between them.
Systems Thinkingis the art and science of making reliable inferences about behavior by developing an increasingly deep understanding of underlying structure. Barry Richmond
Feedback loops help us understand how things interact and build systems for the Internet of Things
Activity
Think of a system in your SMART City. Draw its parts and their interactions.
The internet of things

The internet of things can be thought of a system or a network of ‘things’ connected to together by the ‘Internet’ thus its name the Internet of Things (or IoT for Short).
Using our systems thinking minds we can breakdown the parts of the IoT system in to some key parts:
The world of Electronics
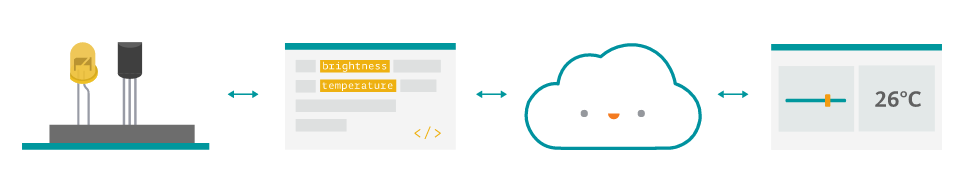
SMART Cities and the Internet of Things
The Internet of Things plays a key part in Smart Cities and opens up many possibilities for innovation, making cites great places to live.
Here are some examples:

Road traffic
Sensors in cars and along roads help ensure safe and efficient travel. These sensors provide valuable information to adjust traffic lights, provide speed recommendations to cars etc.

Houses
IoT devices enable householders to automate and control many aspects of their home including lighting, air conditioning and garden watering. Both from the home and remotely.
Public transport
The data from IoT sensors can help to identify how public transport is used. This data allows transport providers to optimise the number and frequency of vesicles, trains to meet commuter demand on the service.

Utilities
The application of sensors in public utilities like electricity, gas and water can help householders to understand and optimise their power usage. Smart Meters send the data to the public utility providing accurate usage readings.

Street lighting
IoT enabled street lights help use historical and real time data to minimise power consumption and maximise safety of pedestrians.

Waste management
The application of sensors in bins help optimise the collection of waste. By monitoring the level of waste in bins a waste removal driver can be notified of which bins are full and eliminate the collection of empty and half full bins.

Environment
Sensors can monitor the environment including water and air quality and provide critical feedback to authorities and citizens.

Public Safety
IoT technologies like CCTV and acoustic sensor allow real-time monitoring, analysis and reporting of events that may effect public safety.
Activity
Can you think of an application of the Internet of Things for your city?
In a few sentences describe your idea.


